How To Turn Off Rear O2 Sensors?
Is it okay to turn off an O2 sensor? Disabling the oxygen sensors can have a number of negative effects on the performance and emissions of your vehicle. Oxygen sensors, also known as O2 sensors, are in charge of measuring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system and transmitting that data to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU then uses that data to optimize the engine’s performance and reduce emissions by adjusting the fuel-to-air ratio.
So it is not advised to turn off the O2 sensors of any of the vehicles. But if you still want to turn off any O2 sensor, especially the rear O2 sensors, then you will find out how it is done in this article. So stick around until the end to find out what you’ve been looking for.
What happens when you unplug/turn off O2 sensors?
If the oxygen sensors are turned off, the engine will not receive accurate information about the oxygen levels in the exhaust and will be unable to properly adjust the fuel-to-air ratio. This can result in a variety of problems, including:
- Poor engine performance: If the fuel-to-air ratio is not optimal, the engine may run poorly or stall.
- Increased emissions: Without the oxygen sensors, the engine will be unable to effectively reduce emissions.
- Increased fuel consumption: If the engine is not running properly, it may consume more fuel than necessary, resulting in lower fuel economy.
- Catalytic converter damage: The catalytic converter relies on oxygen sensors to function properly, and disabling the sensors can cause damage to the converter, which can be expensive to repair.
It’s worth noting that tampering with the emissions system, including turning off the oxygen sensors, is illegal in many states and countries.
It’s always best to seek advice from a professional mechanic or the vehicle’s manufacturer on how to properly diagnose and repair any oxygen sensor issues.
How To Turn Off Rear O2 Sensors on your own?
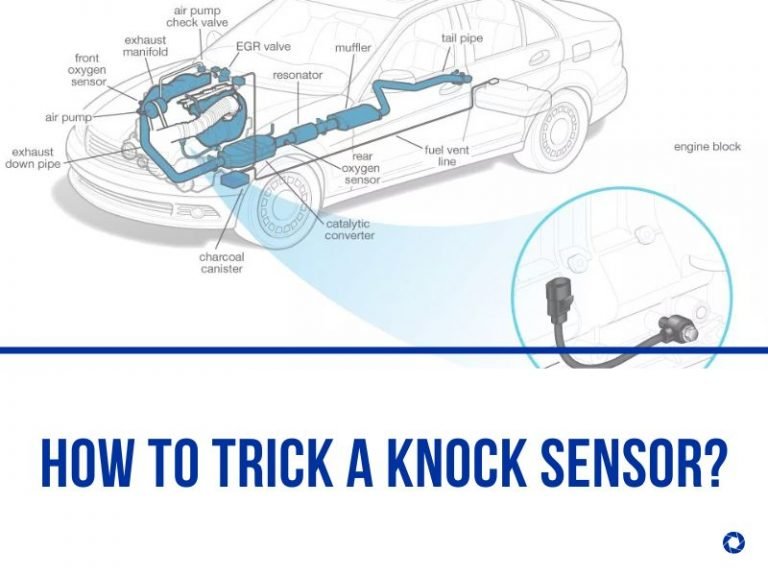
Step 01: Find your car’s O2 sensors there. Each car contains at least one oxygen sensor, although the majority have four.

Step 02: Examine the down tube that emerges from the exhaust manifolds and both exhaust manifolds. Each manifold and down tube presumably contain one sensor. The O2 sensor has a green wire sticking out of the top and is shaped like a white spark plug.
Step 03: Find the wiring harness that connects to the O2 sensor by following the green cable that comes from it.
Step 04: To make a loop out of the green wire, unplug the O2 sensor from the electrical harness.
Can you bypass the O2 sensor?
It is not advised to bypass oxygen sensors because it can have a negative impact on your car’s performance and emissions and is prohibited in many states and countries. The engine control unit (ECU) uses the oxygen sensors (O2 sensors) to measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system and send that data to the ECU so that the ECU can adjust the air-to-fuel ratio for optimum engine performance and lower emissions.
It is crucial to have your oxygen sensors correctly identified and fixed by a qualified mechanic if you are having issues with them. The sensors might occasionally just need to be cleaned or replaced.
How to bypass the 02 sensors?
Even so, doing so is not advised because it could harm the engine and catalytic converter and cause the emissions test to fail. If you insist on bypassing the oxygen sensor, you can do it by using a simulator or dummy sensor.
Step 02: Locate the necessary O2 sensor for removal. It looks like a plug and belongs in the exhaust system. It may be controlled by two different sensors and be located in the catalytic converter or both before and after it.
Step 02: Take care when unplugging the sensor’s wiring. Before you can remove the tab from its housing, you must squeeze it to release it. Finally, using a unique tool for oxygen sensor removal, turn it counterclockwise.
Step 03: Install your new O2 sensor simulator, also known as a dummy sensor. As if you were installing a new O2 sensor, you insert it by rotating the sensor clockwise.
It’s crucial to remember that it’s against the law in many states and nations to tamper with the emissions system, including bypassing the oxygen sensors. This may affect your vehicle’s warranty and resale value and result in fines, penalties, or even criminal charges.
Can you run a car without a downstream O2 sensor?
A car can technically operate without a downstream oxygen sensor (O2 sensor), but this is not recommended because it can impair the vehicle’s performance and emissions.
The downstream oxygen sensor is in charge of measuring the levels of oxygen in the exhaust after it exits the catalytic converter. The engine control unit (ECU) uses this data to adjust the air-to-fuel ratio for optimal engine performance and lower emissions.
What happens when the O2 sensor fails to perform?
If the downstream oxygen sensor fails or is disconnected, the engine will not receive accurate information about the oxygen levels in the exhaust and will be unable to properly adjust the air-to-fuel ratio. This can result in a variety of problems, including:
- Poor engine performance: If the air-to-fuel ratio is not optimal, the engine may run poorly or stall.
- Increased emissions: Without the downstream oxygen sensor, the engine will be unable to effectively reduce emissions.
- Increased fuel consumption: If the engine is not running properly, it may consume more fuel than necessary, resulting in lower fuel economy.
- Catalytic converter damage: The catalytic converter is dependent on the downstream oxygen sensor to function properly, and disabling the sensor can cause damage to the converter, which can be expensive to repair.
Tampering with the emissions system, including disabling the downstream oxygen sensor, is illegal in many states and countries. This can result in fines, penalties, and even criminal charges, as well as affecting the warranty and resale value of your vehicle.
It’s always best to seek advice from a professional mechanic or the vehicle’s manufacturer on how to properly diagnose and repair any oxygen sensor issues.